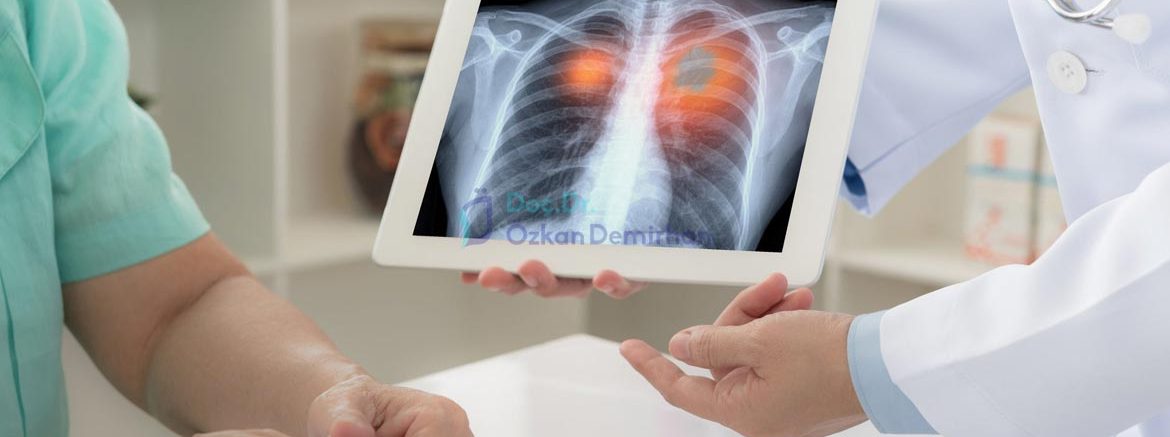
The lung has two parts, the right and left lung. The right lung is slightly larger, because the left lung is located with the heart. The left lung consists of 8 segments and the right lung consists of 10 segments. Both lungs have at least one fissure. Fissures divide the lung into smaller lobes.
The left lung is divided into two by a single fissure, the upper and lower lobes. The right lung has two fissures, one major and one minor: these fissures form three lobes: upper, middle, and lower. Sometimes it is the azygos lobe as a variation of normal anatomy.
The azygos lobe is usually located at the apex of the right lung. The left and right lung lobes are divided into segments representing the lung areas in which different bronchioles function. Right and left main bronchi emerge from the tracheal bifurcation (carina), and each main bronchus enters the hilum of its own lungs. These then divide into lobar bronchi and then into smaller airways called bronchioles, forming a root-like network. This network extends to the entire spongy tissue of the lung.